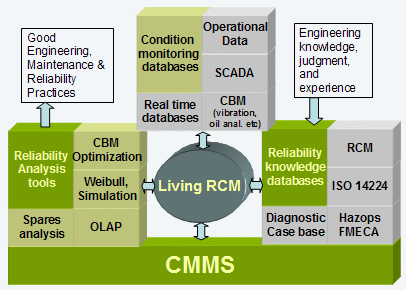
The diagram illustrates that effective physical asset management depends on several categories of information and knowledge.
Components in the LRCM continuous improvement cycle
The diagram points out the interaction among the standard components of maintenance management. These include:
-
Knowledge base development (FMECA/RCM, troubleshooting aids, failure code tables, and safety related knowledge/)
-
Work order management
-
Condition and operation monitoring
-
Analytic procedures
These four classes of systems must work in harmony. Maintenance strategic knowledge grows through the analysis of CMMS and condition /operational monitoring databases. Knowledge derives from the analysis of work order instances of RCM failure modes.
The blocks on the left represent the analyical tools available to a maintenance department. But they are unusable without knowledge of failure modes represented by discrete RCM records. The CMMS records the occurrence of each unit of knowledge (failure mode) in precise RCM terms. Such RCM precision results from having described the failure mode in the context of the Function to be maintained, the way that function has been compromised (the Failure), and the relevant information surrounding the event that caused the failure (the Effects).
The analysis tools and knowledge bases are represented by the left and right diagram blocks respectively. The monitoring systems are in the top group of blocks. The CMMS supports the other three groups and is depicted as a foundational block. At the hub, linking all four components, the Living RCM system that ensures that work orders represent true “instances” of knowledge records (failure modes). In this way those instances can be analyzed (“counted”) using a variety of Reliability Analysis tools. The analysis will improve maintenance based on evidence by modifing age and condition based tasks.
© 2011, Murray Wiseman. All rights reserved.
