One of LRCM’s purposes is to guarantee high quality information from the CMMS with which to perform Reliability Analysis (RA). Systematic improvement of maintenance performance comes mainly from RA. RA analyzes and models the factors influencing failure in order to develop decision policies. RA also measures the performance of those maintenance decision policies, so that they can be improved on a continuous cycle.
The lack of adequate information in the CMMS has impeded RA and decision modeling since its inception in the late 1970s because the CMMS developers did not address the vital issue of quality information for RA. Instead they assumed that hastily conceived failure codes would be adequate for subsequent Reliability Analysis. Most managers and engineers admit that failure codes never worked and blame the poor information in the CMMS for their inability to advance maintenance strategy. The codes were either too general or too specific and did not provide technicians with an accurate way of representing the “as found” state of the equipment. Technicians often used the default code “other” when completing their work order form. They became frustrated and as a result did not consider the drop down lists of codes as a serious method to record historical failure mode data.
RCM is the simplest way to describe a maintenance event accurately. That is because RCM describes the failure mode as precisely as needed. The RCM description includes the context as defined by function, failure, effects, and consequences associated with the failure mode.
By using the LRCM user interface (shown below) when closing work orders, the technician can for the first time translate his observations exactly and conveniently into the CMMS. All CMMS codes are mapped transparently to the RCM hierarchy.
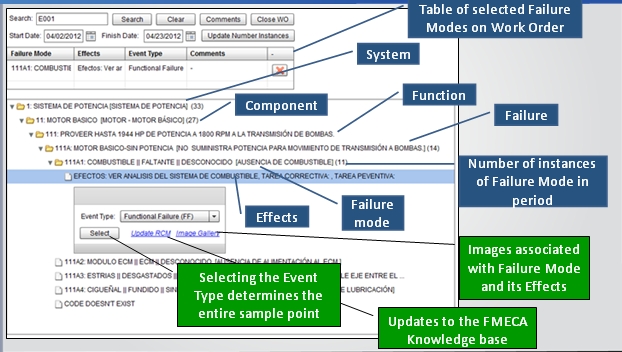
The second important purpose of LRCM is the dynamic update of the organization’s RCM knowledge. This is done directly from the LRCM UI by hitting “Update RCM”. The user is then provided with a second screen which allows him to edit or propose new RCM knowledge. The software manages quality control, authorization, and tracking of all changes in RCM. The state of knowledge at any previous time can be displayed, which can be important for the investigation of HSE incidents.
© 2012, Murray Wiseman. All rights reserved.